InfluxDB: Flux - Aggregation Function reduce(): Unterschied zwischen den Versionen
Aus Wiki-WebPerfect
Admin (Diskussion | Beiträge) |
Admin (Diskussion | Beiträge) K (Admin verschob die Seite InfluxDB: Flux - Function reduce() nach InfluxDB: Flux - Aggregation Function reduce(), ohne dabei eine Weiterleitung anzulegen) |
||
| (6 dazwischenliegende Versionen des gleichen Benutzers werden nicht angezeigt) | |||
| Zeile 1: | Zeile 1: | ||
== When should I use reduce() == | == When should I use reduce() == | ||
| + | The aggregation function "reduce()" is useful if you want to aggregate (sum, count,..) foreach series. <br> | ||
| + | For example you have multiple Clusters with multiple Nodes in it and you want to calculate how many Nodes are in each Cluster and also calculate the sum of a "_value" field, then you can use reduce(). <br> | ||
| + | ''I think it is more clearly when you have read the example below.'' | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Important == | ||
| + | By default, reduce() drops any columns that: | ||
| + | *Are not part of the input table’s group key. | ||
| + | *Are not explicitly mapped in the reduce() function. | ||
| Zeile 7: | Zeile 15: | ||
=== Flux === | === Flux === | ||
| + | <pre> | ||
bucket = "<YOUR_BUCKET>" | bucket = "<YOUR_BUCKET>" | ||
| Zeile 13: | Zeile 22: | ||
|> filter(fn: (r) => | |> filter(fn: (r) => | ||
r._measurement == "asset_hyperv_local" and | r._measurement == "asset_hyperv_local" and | ||
| − | r._field == "physicalmemory" | + | r._field == "physicalmemory" |
| − | + | ||
) | ) | ||
|> last() | |> last() | ||
| Zeile 21: | Zeile 29: | ||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
| + | [[Datei:00-before reduce.png]] | ||
| − | === Flux with | + | |
| + | === Same Flux Query but with "reduce()" in action === | ||
<pre> | <pre> | ||
bucket = "<YOUR_BUCKET>" | bucket = "<YOUR_BUCKET>" | ||
| Zeile 31: | Zeile 41: | ||
|> filter(fn: (r) => | |> filter(fn: (r) => | ||
r._measurement == "asset_hyperv_local" and | r._measurement == "asset_hyperv_local" and | ||
| − | r._field == "physicalmemory" | + | r._field == "physicalmemory" |
| − | + | ||
) | ) | ||
|> last() | |> last() | ||
| Zeile 45: | Zeile 54: | ||
) | ) | ||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Datei:01-after reduce.png]] | ||
| + | ''Influxdata documentation: https://docs.influxdata.com/influxdb/v2.0/reference/flux/stdlib/built-in/transformations/aggregates/reduce/'' | ||
[[Kategorie:TIG-Stack]] | [[Kategorie:TIG-Stack]] | ||
Aktuelle Version vom 19. Mai 2021, 14:08 Uhr
Inhaltsverzeichnis
[Verbergen]When should I use reduce()
The aggregation function "reduce()" is useful if you want to aggregate (sum, count,..) foreach series.
For example you have multiple Clusters with multiple Nodes in it and you want to calculate how many Nodes are in each Cluster and also calculate the sum of a "_value" field, then you can use reduce().
I think it is more clearly when you have read the example below.
Important
By default, reduce() drops any columns that:
- Are not part of the input table’s group key.
- Are not explicitly mapped in the reduce() function.
Example
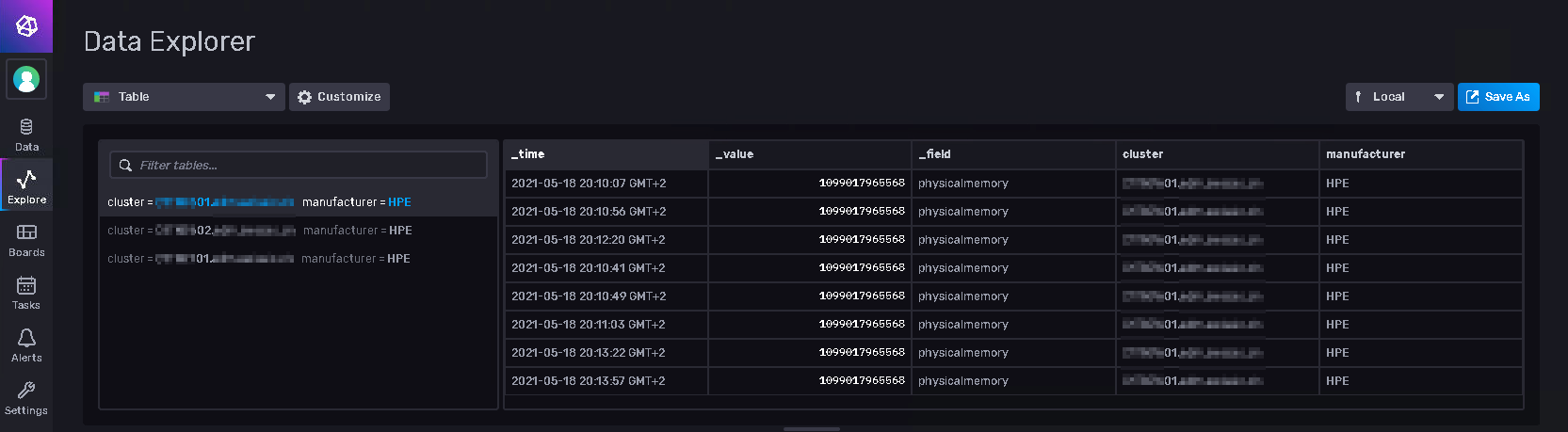
Because the raw data in my example measurement "asset_hyperv_local" has a lot of tags I use "keep()" to decrease the number of columns.
Flux
bucket = "<YOUR_BUCKET>"
from(bucket: bucket)
|> range(start: v.timeRangeStart, stop: v.timeRangeStop)
|> filter(fn: (r) =>
r._measurement == "asset_hyperv_local" and
r._field == "physicalmemory"
)
|> last()
|> group(columns: ["cluster", "manufacturer"])
|> keep(columns: ["_time", "_value", "cluster", "manufacturer", "_field"])
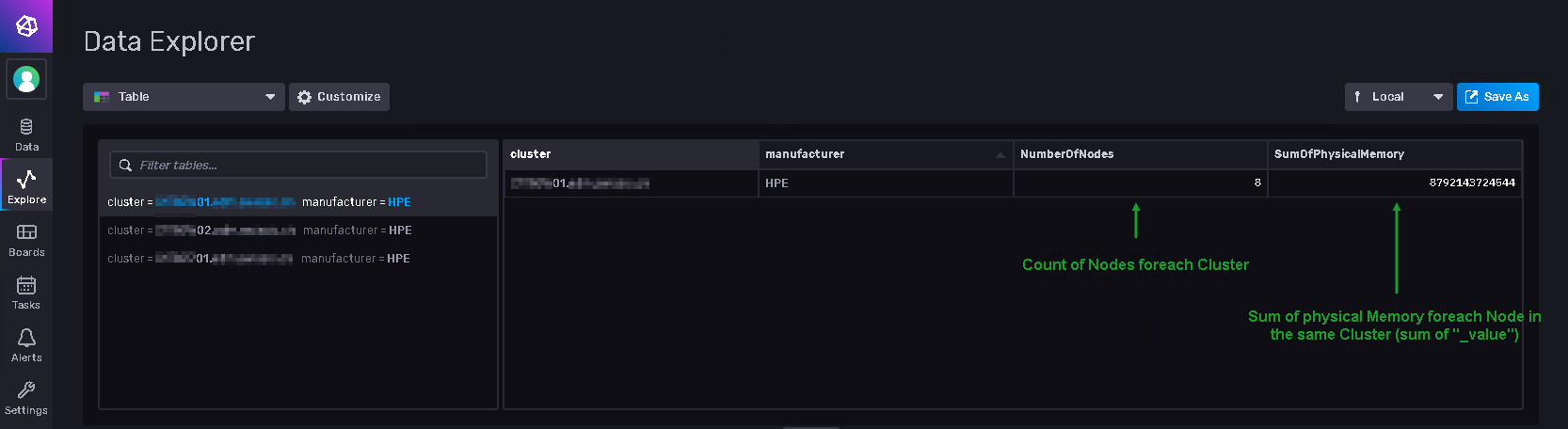
Same Flux Query but with "reduce()" in action
bucket = "<YOUR_BUCKET>"
from(bucket: bucket)
|> range(start: v.timeRangeStart, stop: v.timeRangeStop)
|> filter(fn: (r) =>
r._measurement == "asset_hyperv_local" and
r._field == "physicalmemory"
)
|> last()
|> group(columns: ["cluster", "manufacturer"])
|> keep(columns: ["_time", "_value", "cluster", "manufacturer", "_field"])
|> reduce(
fn: (r, accumulator) => ({
NumberOfNodes: accumulator.NumberOfNodes + 1.0,
SumOfPhysicalMemory: r._value + accumulator.SumOfPhysicalMemory,
}),
identity: {NumberOfNodes: 0.0, SumOfPhysicalMemory: 0.0}
)
Influxdata documentation: https://docs.influxdata.com/influxdb/v2.0/reference/flux/stdlib/built-in/transformations/aggregates/reduce/